Renewable power sources like biomass, geothermal, ocean, sun based energy, wind energy and hydro-power have enough capacity to solve the energy crisis for the whole world.
International organizations such as the United Nations endorse the use of renewable energy because it strengthens the nation’s energy security, enhances economic growth and reduces carbon emissions.
Many countries now see renewable energy as the future of our energy resources.
So let’s explore what renewable energy is, its uses, benefits, types,etc.
Also Read: 8 Latest Trends in Electrical Engineering
What is renewable energy resource?

Defining renewable energy sources accurately proves to be a complex task, mainly owing to the presence of a wide range of energy resources and options, coupled with diverse objectives that advocate for their utilization.
So to understand, let’s see how three major international organizations define renewable energy.
Which are,
- US Energy Information and Administration (EIA)
- United Nations (UN)
- International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA)
As per US Energy Information and Administration (EIA)
The US Energy Information and Administration (EIA) which provides authoritative data analysis, policy recommendation and real world energy solutions defines renewable energy resources as an,
“Energy from sources that are naturally replenishing but flow-limited; renewable resources are virtually inexhaustible in duration but limited in the amount of energy that is available per unit of time”.
The above passage informs us that Renewable energy refers to the energy derived from sources that are naturally replenished. However, they are flow-limited, meaning that the amount of energy they can provide at any given time is limited.
Also, while renewable resources can provide energy continuously over long periods, the rate at which they generate energy is not constant or controllable.
For example, solar energy depends on the availability of sunlight, which varies depending on the time of day, weather conditions, and geographic location. Similarly, wind energy relies on the strength and consistency of wind patterns.
As per United Nations (UN)
The United Nations (UN) define Renewable energy as follows,
“An energy derived from natural sources that are replenished at a higher rate than they are consumed. Sunlight and wind, for example, are such sources that are constantly being replenished. Renewable energy sources are plentiful and all around us.”
According to the above verse, Renewable energy refers to energy that is derived from natural sources that are replenished at a faster rate than they are consumed.
Examples of such sources include sunlight and wind. These resources are constantly being renewed or regenerated, making them sustainable in the long term.
Further, it also tells us that unlike traditional fossil fuels, renewable energy sources are abundant and readily available.
For instance, sunlight is constantly emitted by the sun and wind is created by natural atmospheric processes. These sources exist in vast quantities and are spread throughout the Earth.
As per International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA)
Finally, The International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) an intergovernmental organization which supports countries in their transition to renewables has a statutory definition given below,
“Renewable energy includes all forms of energy produced from renewable sources in a sustainable manner, including bio-energy, geothermal energy, hydro-power, ocean energy, solar energy and wind energy.”
The extract does not talk about renewable energy being inexhaustible or replenishing.
But it only explains that renewable energy encompasses a wide range of energy forms that are derived from sustainable and renewable sources. These sources include bio-energy, geothermal energy, hydro-power, ocean energy, solar energy, and wind energy.
Also Read: Explained | Top 7 Solar Energy technologies
Summary of definitions
If you carefully study the definitions you will notice that they are different from each other but give us a fair idea of what represents a renewable energy source.
So summarizing the above definitions we get,
- Renewable energy sources naturally replenished themselves, but being flow-limited, the amount of energy they can provide at any given time is limited
- Renewable resources can provide sustained energy over long periods but the rate at which they generate energy is not constant or controllable.
- A form of energy derived from the sun, the wind, water, the Earth’s heat, and plants.
- The term renewable energy refers to biomass energy, hydro energy, solar energy, wind energy, geothermal energy, and ocean energy
- Renewable energy technologies convert these energy sources into forms of energy that we can use, such as electricity, heat, chemicals, or mechanical power.
- These sources get replenished by natural processes at a rate faster than its use.
Types of renewable energy sources
There are several types of renewable energy sources:
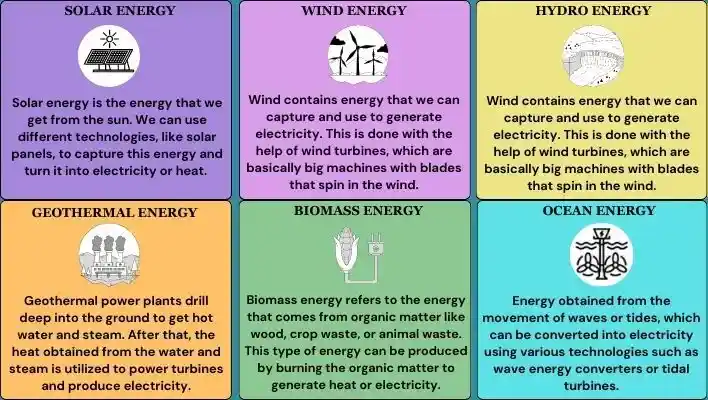
Solar energy
Solar energy is the energy that we get from the sun. We can use different technologies, like solar panels, to capture this energy and turn it into electricity or heat. It can be used for all kinds of things, like powering our homes, businesses, and even vehicles.
Solar energy can be harnessed various ways. One popular method is by using solar panels, which capture the sun’s energy and convert it into electricity or heat.
Wind energy
Wind contains energy that we can capture and use to generate electricity. This is done with the help of wind turbines, which are basically big machines with blades that spin in the wind.
The spinning blades of the wind turbine generate kinetic energy, which is then converted into electrical energy. This is what we call wind power, and it’s a really good source of renewable and clean energy.
Hydro energy
Water can flow really fast or fall from great heights. This type of force and movement can actually create energy that we can use to generate electricity. Hydroelectric power plants are constructed containing big machines that use the force of falling or flowing water to turn turbines and generate electricity.
Geothermal energy
Geothermal power plants drill deep into the ground to get hot water and steam. After that, the heat obtained from the water and steam is utilized to power turbines and produce electricity.
Biomass energy
Biomass energy refers to the energy that comes from organic matter like wood, crop waste, or animal waste. This type of energy can be produced by burning the organic matter to generate heat or electricity.
Ocean energy
Energy obtained from the movement of waves or tides, which can be converted into electricity using various technologies such as wave energy converters or tidal turbines.
Also Read: Wind Energy 101: Explore the Basics of a Sustainable Future
Which is the Best source of renewable energy?
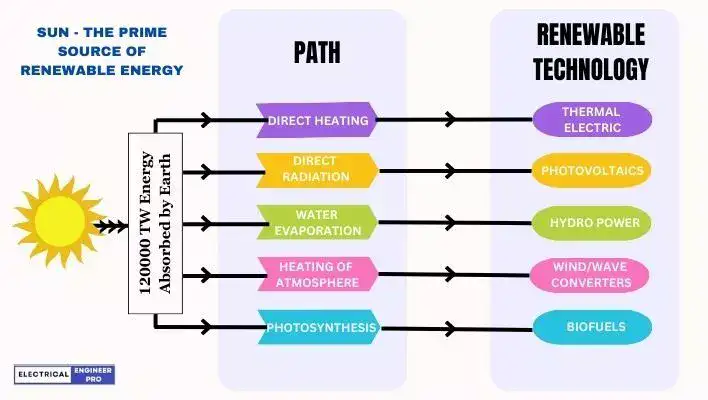
So, basically, when we talk about renewable energy, there are a lot of things to consider.
Factors like location, availability, and technological advancements all play a big role in determining which renewable energy source is the best.
That being said, right now, solar energy is the most favored and productive renewable energy source out there.
After all, Sun is a perfect representation of renewable energy sources because it’s always there, it’s free and we’re never going to run out of it!
The thing is, a lot of other renewable energy sources actually come from the sun in some way, too.
For example, wind is created when the sun heats up the earth’s atmosphere unevenly, which creates differences in air pressure that then cause the wind to blow.
Biomass energy comes from plants that use sunlight to grow, while hydro power is generated by water that moves through rivers and streams, which happens because of the water cycle that’s powered by the sun.
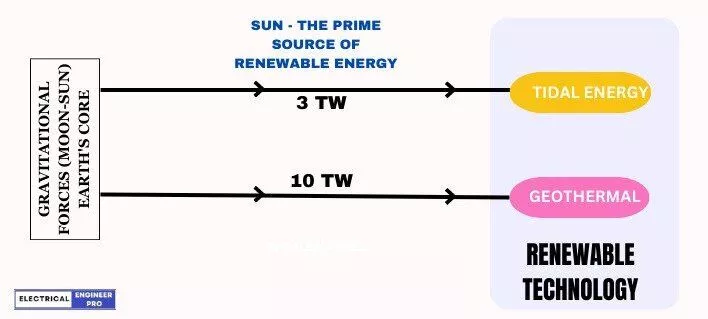
Geothermal energy is also partially influenced by solar energy. It relies on two primary sources to supply heat energy to the ground: the Earth’s crust and the sun’s solar energy.
One way of using geothermal energy is called the shallow geothermal energy method. This method makes use of both the sun’s energy that reaches the Earth’s surface and the heat from the Earth’s core.
Heat pump is used to take advantage of the natural warmth in the ground to provide heat in the winter, and can even reverse the process to cool the air during hot summer months.
Hence, geothermal energy is primarily generated by heat inside the Earth but also be partially influenced by the sun’s energy
Like geothermal energy, Tidal / Ocean energy is too partially influenced by the Sun.
As the Earth, Moon and Sun orbit each other in space, their gravitational pull causes large amounts of water to move around the Earth’s oceans. These shifts in the bodies of water create vertical movements that we know as tides.
Tidal energy systems take advantage of these movements by using water wheels and turbines, similar to those used in hydroelectricity generation. Unlike other systems, tidal energy can generate power in both directions, when the water flows in and when it flows out.
So, long story short, the sun is pretty much the MVP of renewable energy sources!
Importance of renewable Energy
Renewable energy plays a vital role in the world’s transition towards a sustainable future.
Below are the seven reasons why transitioning to renewable energy is the only way to ensure a healthy world for present and future generations.
Also Read: Guide to Geothermal Energy | How Earth’s Power is Harnessed?
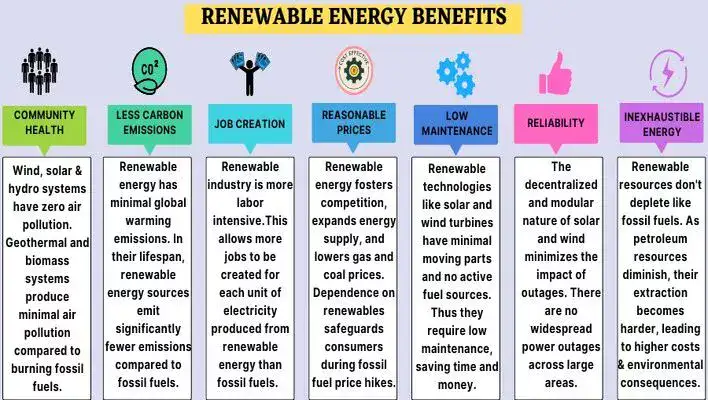
- Community health
Respiratory problems, brain damage, weak hearts, cancer, untimely deaths and numerous serious problems are attributed to air and water pollution from burning of fossil fuels like coal and natural gas. In the case of clean energy technologies, they do not produce harmful effects that burning of fossil fuels create.
No air pollution is associated with Wind, Solar and Hydro systems. Geothermal and biomass systems produce some air pollution but it is much lower than from burning of fossil fuels.
Also wind and solar do not need water to maintain and operate. As their functioning is free of water they do contaminate drinking water or agricultural land.
In comparison fossil fuels can have a notable effect on water supplies. Coal and natural gas mining contaminate water used for consumption.
- Reduced carbon emissions
Human affairs are responsible for loading our planet with CO2 and other GHG emissions. These gases act as insulation to trap heat. The outcome of human activities has led to damaging effects ranging from intense storms, droughts, rise in sea level and extinction of wildlife.
In many nations, the electricity sector is majorly responsible for global warming. Most of these countries utilize fossil fuels like coal and gas to generate electricity.
Global warming emissions are little to none in renewable energy. In the total life span of renewable energy, the emissions produced by them are considerably less than fossil fuels.
A transition towards renewable energy will enable us to move away from carbon intensive energy sources and assist us to decrease emissions associated with global warming.
- Job creation and Economic welfare
The fossil fuel industry is highly mechanized and automated. Whereas the renewable industry is more labor intensive.
Be it solar PV or wind farms the labor demand is more as these projects are located in remote areas where much automated machines are not required. This allows more jobs to be created for each unit of electricity produced from renewable energy than from fossil fuels.
Along with job creation, it can also create positive economic effects to local governments and small businesses. For instance small businessmen will benefit from increased household incomes. Local governments will also get rewarded in the form of building contracts and taxes from the renewable industry.
The landlords will get rent and payments from the renewable industry if the projects use their lands. Also land owners can create wealth by producing feed-stocks from biomass power plants.
- Reasonable prices
Renewables provide cheap electricity and can help rationalize energy prices in the future..
However, renewable energy needs high initial investment to built but their operating costs are low. Also they do not need fuels like gas or coal to generate electricity so the energy costs will get stabilized over time.
As the renewable technologies market is more developed and widely used, the prices are likely to drop even more.
Using renewable energy can decrease the prices of gas and coal by creating competitiveness and expanding energy supply. Being reliant on renewable energy can help protect consumers when fossil fuel prices rise.
- Low maintenance
To a great extent, renewable energy technologies require less overall maintenance than conventional fossil fuel generators.
In fact, renewable technologies such as solar and wind turbines have little to nothing in terms of moving parts and do not depend on active fuel sources. Fewer maintenance requirements contribute to saving time and money.
- Reliability
The distributed and modular designs of renewables such solar and wind result in small scale outages. A fault in a part of a solar array or a couple of windmills going dead in wind farms will not lead to large scale power outages over large areas.
Distributed systems means the renewables are spread over a large geographical area. Therefore, extreme weather conditions in one area will not cut off power in the whole region.
Modular system means the renewables are made up of many independent wind turbines or solar arrays. Hence, even if some components in the system are damaged, others can continue to work.
- Inexhaustible energy
A strong wind, a sunny climate, plentiful crops, high temperatures of the earth and the rapid movement of water can give a constant source of energy. The electricity coming from these sources are extremely small but the scenario will change in the coming years.
Surveys conducted have conveyed that renewables can supply a remarkable portion of electricity needs even if there are constraints involved.
Renewable resources do not run out, like most forms of fossil fuels. For example, petroleum resources, they will become more difficult to obtain, which will increase the fuel cost and environmental impact.
It is possible that renewable energy sources will grow in importance over the next decade and emerge as a market leader in the power industry. However, upfront investment is essential to get these started and thus can make the process sluggish.
Further, only one renewable source is not enough to replace fossil fuels. A careful study is required to employ a combination of several sustainable options based on its utilization and financial feasibility.
The switch from fossil fuels to renewable energy sources will take time.The transfer from fossil fuels to renewables will not only demand costs but also change in human attitudes and irrational thinking.
The bottom line is that the shift to renewable energy is possible as long as we start to take action quickly.
Advantages of renewable energy
The adoption of Renewable resources has a range of advantages. They are:
- Till the sun is shining renewables will never run out i.e. inexhaustible
- It strengthens energy security and lowers the price of conventional fuels.
- It can be produced locally hence reducing the dependency on imported fuel from countries with volatile governments.
- Emissions are only produced while making and scrapping after its lifespan ends. That means it is practically non-polluting.
- The energy plant can be located near the demand thereby reducing transmission and distribution losses.
- Reliable system because the generation does not depend on one generator like centralized fossil fuel plants.
- Renewables fit in the requirements of developing countries because it is not easier for them to produce energy with conventional fossil fueled power plants.
- Using renewable energy will lead to saving fossil fuel for other applications and for future generations.
Can renewable energy replace fossil fuels?
As you all know, the energy sector is still dominated by fossil fuel and is responsible for over 70% of global greenhouse gas emissions.
The energy pundits predict that the global energy demand will increase by 50% by 2050. Hence it’s obvious that we can no longer depend on fossil fuels if we want to reduce carbon emissions.
So you must be wondering if renewable energy is heading in the right direction to replace fossil fuels.
The answer to that question is YES. It’s not my conclusion but of the IEA.
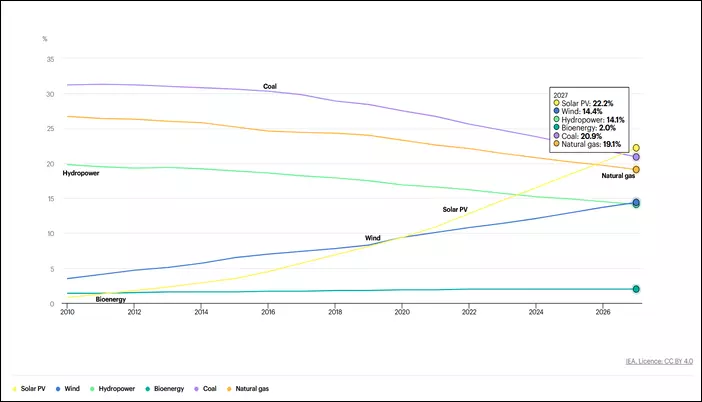
In its latest report, the International Energy Agency (IEA) revealed that total installed capacity of wind and solar is on track to pass natural gas in 2023, coal in 2024 and by 2025 renewables will become the largest source of electricity generation and are expected to supply 33% of the world’s electricity.
Further, the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) suggests that renewable energy will need to supply 80% of the world’s electricity by 2050 to drastically decrease greenhouse gas emissions and prevent climate catastrophe.
This means that the renewable share of global electricity generation should almost triple between 2025 and 2050. The only way to achieve this is by promoting innovation in renewable energy technology.
The surveys done by International organizations confirm that there are remarkable technologies out there which will revolutionize the renewable sector.
For example, Solar industries are developing solar panel roads that could cover miles of highway. Solar farms consisting of solar panels that are floating on the ocean surface.
Floating solar farms are possible because we have already installed floating wind turbines that don’t require fixed foundations and could therefore be used on deep parts of the ocean.
Then there’s blade-less turbine cylinders that are fixed vertically with an elastic rod. The cylinder oscillates on a wind range which then produces electricity. They generate the same amount of electricity as traditional wind turbines but for 40% less money and using less technology.
All the energy generated could be tied together to smart grids which will enable a two-way flow of electricity and pave the way for a fully decentralized energy grid. The innovation in smart grids will ensure that the energy is efficient, secure and affordable.
All the technologies highlighted are not the only ones, there are many more. However most of these technologies have some major flaws to overcome before they could contribute to generating energy.
Many technologies will fail but what is important is that we need this kind of bold innovation and they should be supported by public policy and private Action.
The message here is very clear. Renewables must replace fossil fuels to meet our energy needs and prevent climate catastrophe. Or else mankind has to perish.
Renewable energy problems
Geographical location and weather conditions
Renewable sources of energy are all about working with what nature has to offer. Hence they’re heavily dependent on the geographical location and weather conditions.
Such unpredictability and instability of renewable sources can make generating electricity a bit of a challenge.
However, if the locations are chosen carefully and planned well, this problem can be easily mitigated. Conducting measurements and environmental studies can also help us better understand the conditions and make the most of them.
Lack of capacity to produce electricity
When we compare renewable energy sources to traditional fossil fuels, one of the drawbacks is that they have limited capacity to produce electricity. They can’t generate as much power as fossil fuel power plants.
To overcome this, the world needs to invest more in the development of renewable energy technologies and build more renewable energy plants.
This will help increase their capacity to generate electricity, making them more competitive with traditional fossil fuels.
Renewables Need Larger Area Compared to Fossil Fuel Power Plants
Renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and hydro power require more space than traditional fossil fuel power plants to generate the same amount of electricity.
This is because the ratio of installed power plant capacity or electricity production to the area of land occupied by the plant is lower for renewable energy sources.
For instance, a solar power plant may generate the same amount of electricity as a fossil fuel power plant, but it would require a much larger area of land to do so.
Mainly because solar panels need to be spread out to capture enough sunlight to produce electricity, while fossil fuel plants can generate a lot of power from a smaller area.
Low Efficiency Levels.
Renewable energy sources such as solar and wind, have lower efficiency levels compared to fossil fuels because they are subject to natural variations and unpredictable weather patterns.
For example, solar panels generate less electricity on cloudy days, while wind turbines produce less energy when the wind is calm. These fluctuations can make it challenging to generate a consistent amount of electricity using renewable energy sources.
Further, the technology used to harness renewable energy is still in the early stages of development and has not yet reached the level of efficiency that traditional fossil fuels have achieved over the past century.
Less operational hours compared to Fossil fuels plants.
Renewable energy sources can’t operate at full power all year round like fossil fuel power plants.
In a year with 8760 hours, coal, gas and nuclear power plants can run at full power for up to 7500 hours.
In contrast, renewable energy sources like wind and solar can only run at full power for around 2000 hours per year on average.
This is because renewable energy sources are affected by natural variations and weather conditions, which can reduce their output.
For instance, solar panels generate less energy on cloudy days, and wind turbines generate less energy when the wind is calm.
On the other hand, fossil fuel power plants can produce electricity more consistently because they are not affected by natural variations.
High Cost
One major drawback is that renewables need significant upfront investment to build the energy infrastructure.
On top of that, these facilities often have long depreciation periods, which means it takes a while for them to generate enough income to pay off the initial investment.
In some cases, like with hydroelectric power plants, there may not even be a foreseeable end to the depreciation period.
Therefore, the main challenges for renewable energy projects are the costs of building and operating them over a long period of time, which can impact the return on investment.
High Per Unit Cost.
The unit costs of renewable electricity is high because of the initial investment costs required to build and maintain renewable energy infrastructure.
Renewable energy technologies often require specialized equipment and materials that can be expensive to produce and install.
However, the unit costs of renewable electricity are expected to decrease overtime as the technologies become more widespread and efficient.
Renewable energy Challenges
Although renewable energy sources like solar and wind face challenges, they are not without hope. It’s essential to identify the obstacles that renewables encounter and find the best path to achieve 100% clean energy by 2050.
Bird Killers
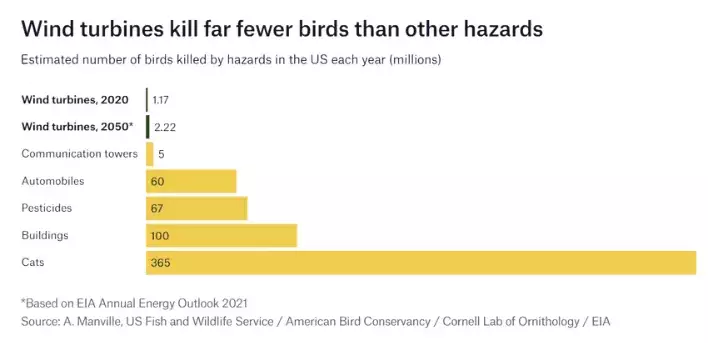
People often criticize wind turbines, claiming that they pose a threat to birds. Unfortunately, this is true. But when you look at the big picture, you might be surprised by the actual numbers.
In 2009, B.K. Sovacool conducted a study called “Contextualizing avian mortality: a preliminary appraisal of bird and bat fatalities from wind, fossil-fuel, and nuclear electricity,”
According to the study, when it comes to bird fatalities, there is no comparison between wind-generated power and fossil fuel-generated power.
The study found that Wind farms are responsible for only 0.3 bird deaths per gigawatt-hour (GWh) of electricity, while fossil-fuel power stations cause 5.2 fatalities per GWh.
This means that power stations using fossil fuels are significantly more harmful to birds, causing 17 times more deaths than wind farms.
If we switch to wind energy instead of fossil fuels, we have the potential to prevent millions of bird deaths.
And here’s an interesting fact: cats actually kill roughly 10,000 times more birds than turbines do. So, when you take into account these numbers, bird deaths caused by wind turbines are comparably small.
Life cycle impacts of renewable technologies.
Some people criticize renewables by pointing out the resources needed to assemble, install, and dismantle solar panels and wind turbines.
They argue that these life cycle impacts make renewables less clean.
There are hundreds of studies published on life cycle assessment of renewable technologies, with variable results.
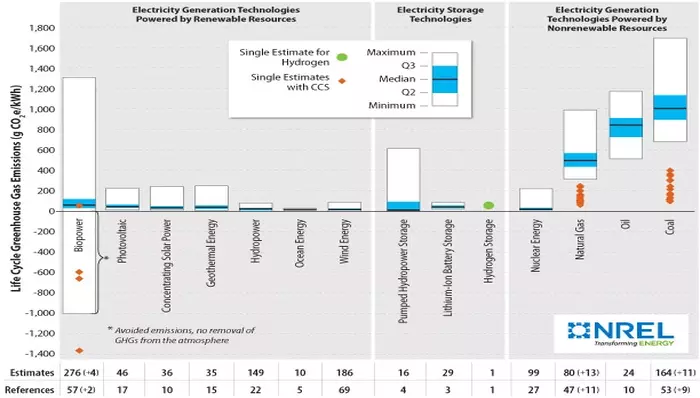
NREL gathered and analyzed a vast amount of data from various sources and found that the greenhouse gas emissions from solar, wind, and nuclear technologies are significantly lower and less variable than emissions from natural gas and coal technologies, which rely on combustion.
This research confirms that despite the amount of materials and concrete needed to build solar and wind energy systems, they can quickly offset the initial carbon emissions.
Moreover, as these renewable technologies continue to improve, they will have a longer lifespan, which will help to mitigate waste issues.
Renewable is not Safe
We get a clear picture of the safest and cleanest sources of energy. The results shows that,
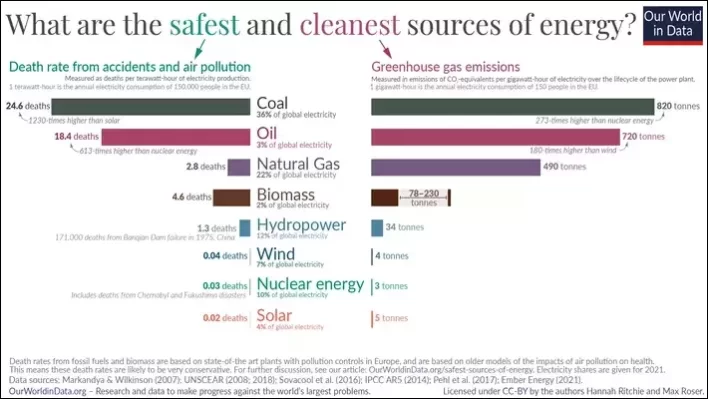
Nuclear energy results in 99.9% fewer deaths than brown coal; 99.8% fewer than coal; 99.7% fewer than oil; and 97.6% fewer than gas. Wind and solar are just as safe.
The study reveals that wind and solar causes 0.02 and 0.04 deaths per terawatt-hour (TWh) of electricity respectively, whereas brown coal causes 32.72 deaths per terawatt-hour (TWh) of electricity.
It’s worth noting that one terawatt-hour is equivalent to the annual electricity consumption of 150,000 people.
This proves that solar and wind energy are safer than fossil fuel power plants.
No energy source is safe because they all have some impact on human health, whether it’s from air pollution or accidents.
However, their contribution to each differs enormously.
In terms of immediate effects, fossil fuels are the most hazardous and polluting since they release the highest amount of greenhouse gases per unit of energy. Therefore, low-carbon energy sources are the safest option with no trade-offs.
In terms of both human health and climate change, it’s more important to move away from fossil fuels than it is to choose between nuclear power or renewable energy.
The focus should be on transitioning to cleaner energy sources that are less harmful to both people and the environment.
Excess Energy
Renewables like wind and solar face a challenge of generating excess energy, especially when we don’t need it.
These sources of energy produce electricity when the sun is shining brightest or the wind is blowing the hardest, which may not coincide with the times we require it.
This mismatch leads to the grid having to dispose of excess energy or risk overburdening the system.
To effectively scale up renewables, countries must also have enough capacity to use the energy these technologies generate.
Interconnection of grids is crucial in enabling states or countries to trade-off excess energy. This way, the grid can transport excess energy to a place where it is needed or stored for later use instead of curtailing or wasting it.
These are the solutions we need to transform our electricity from fossil fuels to renewables quickly.
The scaling of renewables, coupled with proper energy consumption planning, can stabilize their variability, ensuring that electricity is readily available whenever we need it.
It is a simple solution to the problem and if implemented correctly, it can stabilize the variability of renewables.
The future of renewable energy looks promising, with increasing adoption and technological advancements driving its growth. However, challenges remain, including intermittency, energy storage, and initial investment costs. Overcoming these obstacles through innovation and supportive policies is crucial for a clean and sustainable energy future.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the intricate definitions of renewable energy resources provided by major international organizations highlight the various perspectives on sustainability.
Solar energy emerges as a prominent choice due to its constant availability, while the importance of renewables is underlined by their positive impacts on community health, reduced carbon emissions, and economic benefits.
The potential for renewable energy to replace fossil fuels is substantiated by projections from the International Energy Agency (IEA) and International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA). Despite facing challenges such as geographical limitations and intermittency, innovations, supportive policies, and grid interconnection offer solutions for a stable, clean energy future.
Critiques regarding the life cycle impacts of renewable technologies are dispelled, emphasizing their environmental advantages over fossil fuels. Safety comparisons reveal renewables and nuclear energy as significantly safer options. However, challenges persist, including excess energy generation.
In essence, the future of renewable energy appears promising, driven by increasing adoption and technological advancements. Overcoming challenges through continued innovation and policy support is imperative for a successful transition to a sustainable and clean energy landscape.