The question appeared in the paper-3 Energy Manager Exam 2017. The question belongs to the Chapter no 2 – Electric motors of ENERGY EFFICIENCY IN ELECTRICAL UTILITIES portion.
We have provided a thorough explanation of unbalanced voltage in our article mentioned below. To grasp the causes and effects of unbalanced voltage, please click the link provided.
Also Read: Essential Guide to Voltage Unbalance
If you are short on time, here’s a brief overview of unbalanced voltage and its correlation with temperature rise.
Voltage unbalance
Voltage unbalance refers to a condition in an electrical power system where the voltages in a three-phase system are unequal or disproportionate. In a balanced system, the voltage magnitudes and phase angles of the three phases are equal, resulting in equal power distribution. However, in an unbalanced system, the voltage levels in the three phases differ, causing an uneven distribution of power.
What causes Unbalanced Voltage?
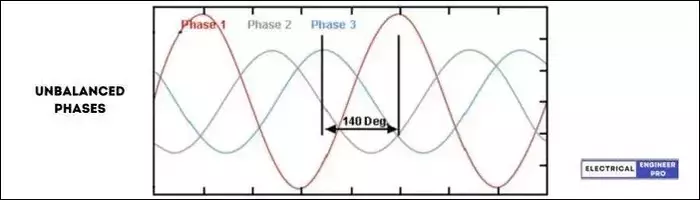
Voltage unbalance can be caused by several factors in an electrical power system. Some common causes include:
Unbalanced loads: When the electrical loads connected to the three phases are not evenly distributed, it can result in voltage unbalance. For example, if one phase has a significantly higher load than the other two phases, it will draw more current, leading to a voltage drop in that phase.
Faulty or imbalanced transformers: Transformers are responsible for distributing power between the phases. If a transformer is faulty or improperly connected, it can introduce voltage unbalance. For instance, a transformer with unequal turns ratios on the primary or secondary side can cause unbalanced voltage.
Damaged or faulty conductors: Faulty or damaged conductors can create differences in impedance between the phases, causing voltage unbalance. Loose connections, corroded wires, or broken conductors can lead to uneven distribution of voltage.
Voltage regulator issues: Voltage regulators are devices used to maintain the desired voltage levels. If a voltage regulator malfunctions or is not properly calibrated, it can result in voltage unbalance.
Single-phase loads: Single-phase loads, such as single-phase motors or appliances, can introduce unbalance in a three-phase system. These loads draw power predominantly from one phase, causing voltage imbalance.
System faults: Faults in the electrical system, such as short circuits or ground faults, can also cause voltage unbalance. These faults can disrupt the normal flow of current and voltage in the system, leading to unbalanced voltages.
Inadequate power supply: Insufficient power supply from the utility or generator can result in voltage unbalance. If the supply voltage to the system is not balanced, it can lead to uneven distribution of voltage among the phases.
Temperature Rise in motors
Voltage unbalance can have a big impact on the flow of electric current and cause significant problems. The difference in current caused by voltage unbalance can be much larger, around 6 to 10 times, compared to the difference in voltage. This means that even a small difference in voltage can lead to a big difference in current flowing through the system.
When a motor runs on a power supply with voltage unbalance, it faces some negative effects, especially related to temperature. The motor tends to get hotter because the voltages in the different phases are not balanced. This increase in temperature happens because there is more current flowing in certain phases, which causes more power to be used and turned into heat.
To understand how voltage unbalance affects motor temperature, let’s take an example. Imagine the voltage unbalance during motor operation is 2% and the initial temperature is 100 degrees Celsius. In this case, the extra temperature increase caused by the voltage unbalance would be around 8 degrees Celsius. So, the motor’s temperature would go up to 108 degrees Celsius.
This rise in temperature is a serious issue because it directly affects the lifespan of the motor’s winding insulation. It is known that for every 10-degree Celsius increase in operating temperature, the insulation life is cut in half. Therefore, the additional temperature rise of 8 degrees Celsius due to voltage unbalance would reduce the insulation life of the motor’s winding by half.
Energy Manager Exam Question
A 75 kW, 415 V, 140 Amp, 4 pole, 50 Hz, 3-phase squirrel cage induction motor has a full load efficiency of 87.6%. The measured operating motor terminal voltages in a 3-phase supply are 415 V, 418 V & 420 V. The current drawn in 3-phase supply are 137 Amp, 132 Amp & 137 Amp. Estimate the additional temperature rise of the motor, due to unbalanced voltage supply. (PAPER – 3 – September, 2017)
Solution
Before estimating the temperature rise of a motor, we have to find the voltage unbalance rate of its operating power supply.
Average Voltage
| Average Voltage (Vavg) | [latex]= \frac{_{Vry + Vyb + Vbr}}{3}[/latex] |
| [latex]= \frac{_{415 + 418 + 420}}{3}[/latex] | |
| = 417.66 V |
Measured Voltage deviation from average voltage.
| Phase | Measured Voltage | Deviation from mean voltage |
| R | 415 | 417.66 – 415 = 2.66 |
| Y | 418 | 417.66 – 418 = – 0.34 |
| B | 420 | 417.66 – 420 = – 2.34 |
Voltage Unbalance %
| Voltage Unbalance % | [latex]= \frac{_{Maximum Deviation from Average Voltage}}{Average Voltage} \times 100[/latex] |
| [latex]= \frac{_{2.66}}{417.66} \times 100[/latex] | |
| [latex]= {0.636}\%[/latex] |
Motor Temperature Rise
| Temperature Rise | = 2 x (% Voltage Unbalance)2 |
| = 2 x (0.636)2 | |
| = 0.80° C |
The additional temperature rise of the motor, due to unbalanced voltage supply is 0.80° C